DOE-NE ASSISTANT SECRETARY DR. HUFF LEAVING DOE IN MAY
ECA thanks Dr Kathryn Huff, Assistant Secretary of the Department of Energy's Nuclear Energy Office, for her leadership and strong support for communities across the DOE complex as she announces her
return to professorship at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
Throughout her tenure, Dr. Huff
has been a champion for advancing nuclear energy - from working to ensure availability of nuclear fuels domestically, supporting advanced nuclear technology developers and restarting the consent-based siting program. Under her leadership, she promoted resources for local elected officials, existing and future and nuclear communities to better understand the myriad opportunities new nuclear development presents and engaging with transparency on issues like cost, fuels, workforce and manufacturing
needs, and nuclear waste management.
ECA appreciates the relationships Dr. Huff has built in our communities during
her time as Assistant Secretary. Dr. Huff. We were especially excited to host her at ECA Forums on New Nuclear Development in Salt Lake City, Utah, and Paducah, KY, where she joined local governments, community leaders and representatives from across the nuclear ecosystem to create the partnerships necessary for new nuclear development and deployment. With Dr. Huff's departure, Dr. Goff will become the Acting Assistant Secretary for Nuclear Energy. He currently serves as the Principal Deputy Assistant Secretary. ECA is excited that Dr. Goff is a keynote speaker at ECA's third New Nuclear Forum: Building
Nuclear Partnerships & Projects in the Tri-Cities, WA, May 8-9. Dr. Huff's announcement at this time of year - and
especially in an election year - is not unusual and serves as a reminder that other political appointees and administration leaders are likely to follow. As leadership changes and transition begins, it is a good time to reflect on successful engagement efforts and how we want to be engaged moving forward.
REGISTER NOW! ECA's New Nuclear Forum: Building Nuclear Partnerships and Projects, May 8-9, 2024 in Kennewick, WA
ECA is excited to be hosting its third New Nuclear Forum, the only meeting designed to bring together DOE, federal, state, local and tribal governments and policymakers with developers, utilities,
regulators, industry, and academia to identify opportunities, challenges and to build the partnerships necessary to support nuclear development. Communities across the country are considering nuclear projects for many reasons - from diversifying regional economies, creating clean energy jobs or meeting carbon reduction goals, to increasing energy security and rebuilding the U.S. supply chain. Some communities have a familiarity with nuclear energy projects, while others are just beginning to evaluate potential interest. The ECA
Forum is designed to enable shared learning so that local, State and Tribal governments evaluating nuclear projects can be meaningfully engaged - and prepared - to match the strengths and needs of their communities with new nuclear opportunities.
INTERESTED IN BEING A SPONSOR? To learn more about sponsorship opportunities, please contact Autumn Bogus, ECA Forum Staff, at abogus@la-inc.com.
QUESTIONS?
For any questions, comments, or to learn more about the ECA New Nuclear Forums, please contact Kara Colton,
ECA Director of Nuclear Policy, at kara.colton@energyca.org or Faith Sanchez, ECA Program Director, at faiths@energyca.org.
NUCLEAR POWER PLANTS: NRC SHOULD TAKE ACTIONS TO FULLY CONSIDER THE POTENTIAL EFFECTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE
Climate change is expected to exacerbate natural hazards—including heat, drought, wildfires, flooding, hurricanes, and sea level rise. In addition, climate change may affect extreme cold weather
events. Risks to nuclear power plants from these hazards include loss of offsite power, damage to systems and equipment, and diminished cooling capacity, potentially resulting in reduced operations or plant shutdowns. Examples of Natural Hazards that May Pose Risks to Nuclear Power Plants
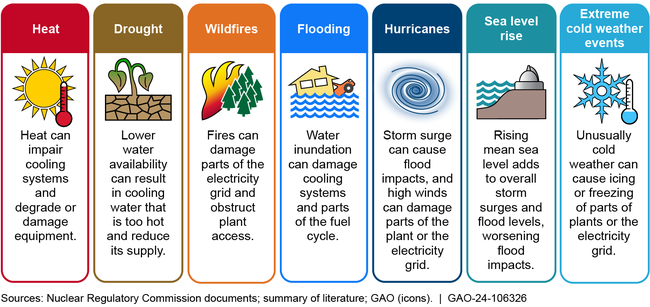 The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) addresses risks to the safety of nuclear power plants, including risks from natural hazards, in its licensing and oversight processes. Following the tsunami that led to the 2011 accident at Japan's Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear
power plant, NRC took additional actions to address risks from natural hazards. These include requiring safety margins in reactor designs, measures to prevent radioactive releases should a natural hazard event exceed what a plant was designed to withstand, and maintenance of backup equipment related to safety functions. However, NRC's actions to address risks from natural hazards do not fully consider potential climate change effects. For example, NRC primarily uses historical data in its licensing and oversight processes rather than climate projections data. NRC officials GAO interviewed said they believe
their current processes provide an adequate margin of safety to address climate risks. However, NRC has not conducted an assessment to demonstrate that this is the case. Assessing its processes to determine whether they adequately address the potential for increased risks from climate change would help ensure NRC fully considers risks to existing and proposed plants. Specifically, identifying any gaps in its processes and developing a plan to address them, including by using climate projections
data, would help ensure that NRC adopts a more comprehensive approach for assessing risks and is better able to fulfill its mission to protect public health and safety. Why GAO Did This StudyNRC licenses and regulates the use of nuclear energy to provide reasonable assurance of adequate protection of public health and safety, to promote the common defense and security, and to
protect the environment. Like all energy infrastructure, nuclear power plants can be affected by disruptions from natural hazards, some of which are likely to be exacerbated by climate change. Most commercial nuclear plants in the United States were built in the 1960s and 1970s, and weather patterns and climate-related risks to these plants have changed since their construction. GAO was asked to review the climate resilience of energy infrastructure. This report examines (1) how climate change is expected to affect nuclear power plants and (2) NRC actions to address risks to nuclear power plants from climate change. GAO
analyzed available federal data and reviewed regulations, agency documents, and relevant literature. GAO interviewed officials from federal agencies, including NRC, the Department of Energy, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and knowledgeable stakeholders from industry, academia, and nongovernmental organizations. GAO also conducted site visits to two plants. Read full report>>
NEW MEDIA: Gone Fission Nuclear Report: National Laboratories Speed Hanford Cleanup April 8, 2024 | S4E7 The Department of Energy’s 17 national laboratories conduct research and development on some of the world’s most vexing challenges—from climate change to the origins of the universe.
Most recently, six labs have turned their attention to speeding cleanup of underground tank waste at DOE’s Hanford site in Washington State. The labs are using $27 million in DOE funding to research everything from tank integrity and the impact of corrosion to robotic handling of tank waste. Estimates show this and other work could save $150 billion in cleanup costs and shave up to two decades off a 60-year timeline. This week, Gone Fission host Michael Butler talks with Connie Herman, Assistant
Director, Savannah River National Laboratory, and Delmar Noyes, DOE Tank Farms Manager at Hanford. NOTE: The work NNLMES performs is being overseen by the EM Laboratory Policy Office with the support of the EM Technology Operations Office, Hanford Site Office as well as the Office of Science, and ARPA-E.
|
Check out ECA's latest
report! DISPOSAL DRIVES CLEANUP: RE-ENERGIZING MOMENTUM FOR DISPOSAL SOLUTIONS FOR RADIOACTIVE WASTE
This report calls on the Department of Energy to launch the initiative to develop the actual waste disposition approaches. The Department could potentially save hundreds of billions of dollars in cleanup costs by using its available tools and implementing the report’s recommendations.
Interactive guide for communities and governments to help navigate nuclear waste cleanup The Energy Communities Alliance (ECA) recently released the Guide to Successful Environmental Cleanup, an interactive online resource that provides frequently asked questions, case studies, and recommendations regarding nuclear waste cleanup. To assist local government officials, their communities, and federal agencies in deciphering
the complexities of the environmental cleanup process, ECA developed this guide to facilitate future successful cleanups.
|
|
|
Stay Current on Activities in the DOE World Read the latest edition of the ECA Bulletin, a regular newsletter providing a detailed brief of ECA activities,
legislative news, and major events from across the DOE complex. Have suggestions for future editions? Email bulletin@energyca.org. |
Learn More about Cleanup Sites with ECA's DOE Site Profiles ECA's new site profiles detail DOE's active Environmental Management cleanup sites and national
laboratories, highlighting their history, missions, and priorities. The profiles are a key source for media, stakeholders, and the public to learn more about DOE site activities, contractors, advisory boards, and their surrounding local governments.
|
|
|
|